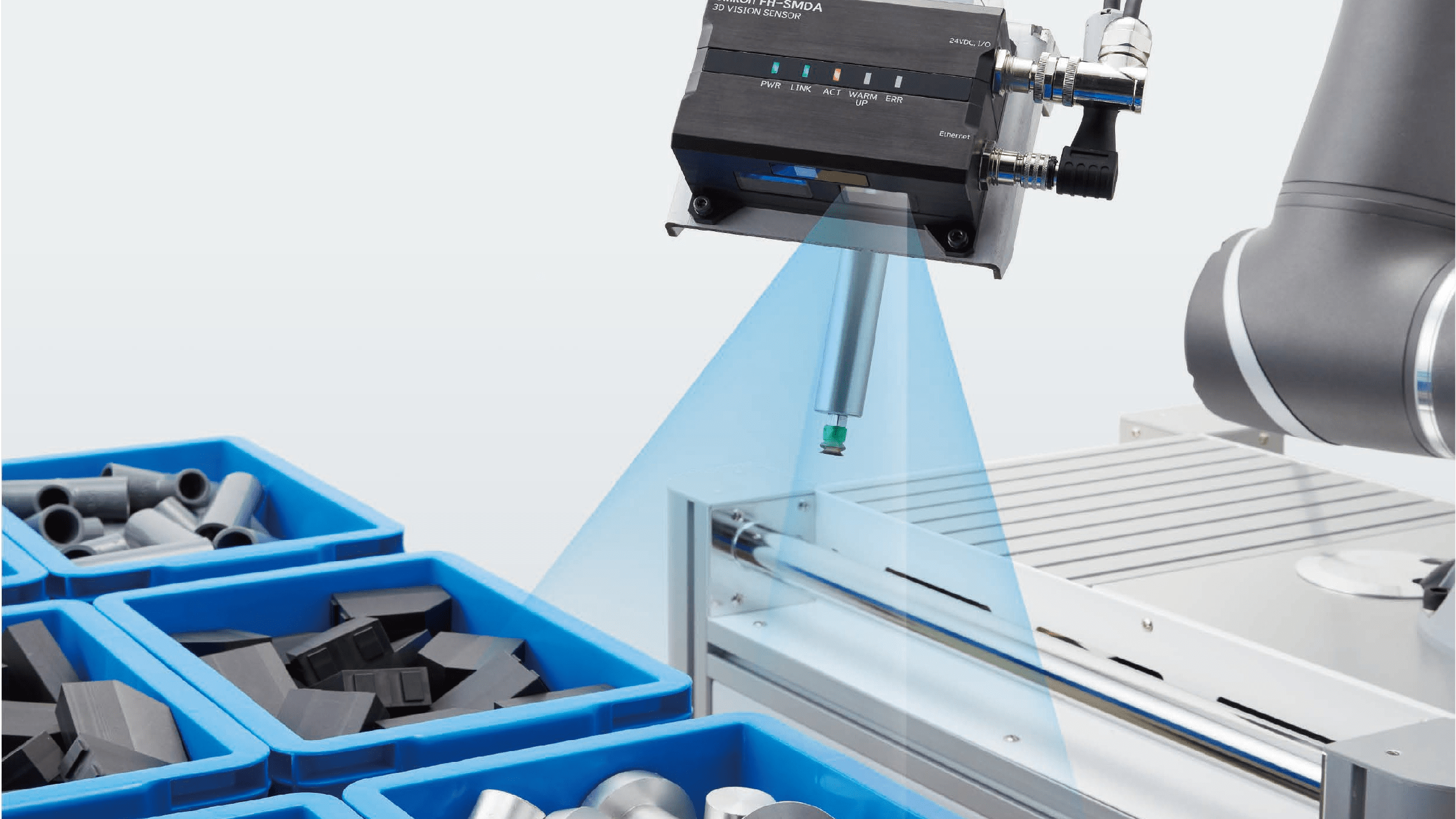
An industrial camera is a heavy-duty device used in industrial applications such as quality control, measurement, and production monitoring in environments like factories and shipyards. Industrial cameras are designed to withstand harsh working conditions far better than standard digital cameras, ensuring reliable operation over extended periods.
These cameras are often used for imaging purposes on long lines, typically ranging from 35 to 60 meters. They are designed to convert optical signals into electrical signals as accurately and completely as possible, even in challenging environmental conditions.
Industrial Cameras: Advantages
- Long-Distance Imaging: Capable of comfortably capturing images over long distances.
- Wide Viewing Angles: Provide imaging capabilities with a 180-degree field of view.
- Problem Detection: Can easily detect issues within pipes or other confined spaces.
- Versatile Use: Suitable for various types of piping and installation systems.
Factors to Consider When Selecting an Industrial Camera:
- Determine the Required Pixel Count:
- For a balanced image processing application: Pixel resolution should be 10 times the preferred measurement tolerance.
- For presence/absence checks: Minimum object field of view should contain at least 500 pixels.
- For code reading applications: The code size should cover three-quarters of the viewing distance.
- Select the Appropriate Transfer Speed:
- In high-speed production processes, the camera’s image transfer speed must be sufficient to capture these processes effectively. Therefore, using high-speed camera systems capable of 250 frames per minute or more is crucial.
- Choose the Camera Size Based on the Installation Area:
- For machines or areas with limited space, selecting a compact camera ensures that the system operates efficiently and systematically.
- Choose Between Black-and-White or Color Cameras Based on Inspection Type:
- Black-and-white cameras are generally preferred for measurement applications. However, color cameras may be advantageous for precise detection, depending on the type of inspection.
- Select the Correct Lens:
- Consider factors such as working and installation distance requirements, focus distance, depth of field according to the target’s height and shape, and lens resolution in relation to the target’s contrast and inspection accuracy.
- Lighting Selection:
- Lighting choice should be based on type, color, target characteristics, control needs, and direction. General steps for selecting lighting include:
- Deciding the lighting direction and type based on the target’s material and shape (e.g., diffuse reflection or specular reflection).
- Determining the size and shape of the lighting according to the reflection type.
- Choosing the wavelength (color) of the lighting.
- Lighting choice should be based on type, color, target characteristics, control needs, and direction. General steps for selecting lighting include:
This approach ensures that you select the most suitable industrial camera for your specific application needs, optimizing performance and reliability in demanding environments.