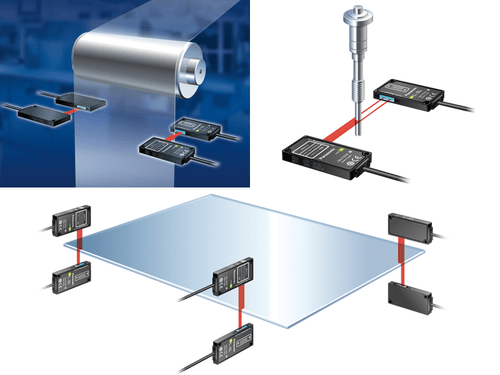
Sensor devices have become crucial in today’s technology landscape, with displacement measurement sensors holding particular significance. The Profiler 2 displacement measurement sensor accurately measures surfaces of objects along the x and z axes, as well as more complex geometries, with high precision. It can simultaneously analyze up to four areas with a single measurement. It is versatile and applicable across various fields. For instance, it allows for the selection of one of ten integrated measurement functions, such as height or width.
Applications of Displacement Measurement Sensors
Displacement measurement sensors offer significant advantages due to their technological advancements and high precision. Their applications include:
- Multi-edge detection
- Measuring shapes and profiles
- Object angle measurement
- Monitoring gap sizes
- Measuring layer thickness in printed circuits
- Measuring the width and thickness of components
- Quality control in the automotive and electronics industries
Operating Principle of Displacement Measurement Sensors
The operating principle of displacement measurement sensors is as follows: A light spot is projected onto the object being measured. The reflected light from the object is captured by a receiver sensitive to light at a specific angle. Using the angle between the transmitter and receiver as a basis, the object’s current position is calculated through mathematical triangular relationships.
Displacement sensors perform measurements by sending laser light to the target object. They are prominent where non-contact measurements are required and are typically used for long-distance measurements. The option to use either reflective or non-reflective configurations provides significant ease of use for the user.
Precision in Displacement Measurement Sensors
Displacement measurement sensors are essential in areas requiring the highest accuracy and quality. They are recognized for their reliability in industrial settings, continually proving their effectiveness as a smart measurement technique. They play a leading role in sensor technology.
Quick Overview of Accurate Measurement
- Simultaneous analysis of up to four areas
- Measurement of complex profiles with a single laser line
- Premium CMOS receiver unit
- Integration of sensor head and evaluation unit in a single device
- Ten integrated measurement functions, including width, slope, and height
- Setup via software or control elements on a display
Advantages of Displacement Measurement Sensors
Maintaining consistent quality during the production of devices and components with varying features requires regular control through measurements. Optical measurement sensors are critical in this regard.
The ability of displacement measurement sensors to perform non-contact, precise, and rapid measurements and directly integrate these results into the production process significantly enhances efficiency. Consequently, production processes achieve higher efficiency without mechanical contact or damage, maintaining the same high quality.